How to Install And Run AFL
Introduction
AFL is an industry standard fuzzing tool, which is widely used by practitioners. For most research tools on fuzzing, such as Angora(S&P’18) and CollAFL(S&P’18), the target is to make fuzzers explore the fuzzed program with higher coverage. These tools added new features to AFL, and were reported to be more effectively and efficiently on finding bugs.
In this post, I will introduce basic usages of AFL.
Download and Install
- To download it, go to the official website or click here.
- Uncompressed the file and run
makeat the source root. - If you want to install it, then run
make install.
Let’s run it!
The most commonly used dataset for fuzzers is LAVA-M. With this dataset, we could test totally four projects: base64, md5sum, uniq and who. For fuzzing we need to compile the projects with afl-clang.
Use the following command to compile the projects:
$ cd lava_corpus/LAVA-M/base64/coreutils-8.24-lava-safe/
$ CC=/xx/afl-clang ./configure
$ make
$ ls src/base64
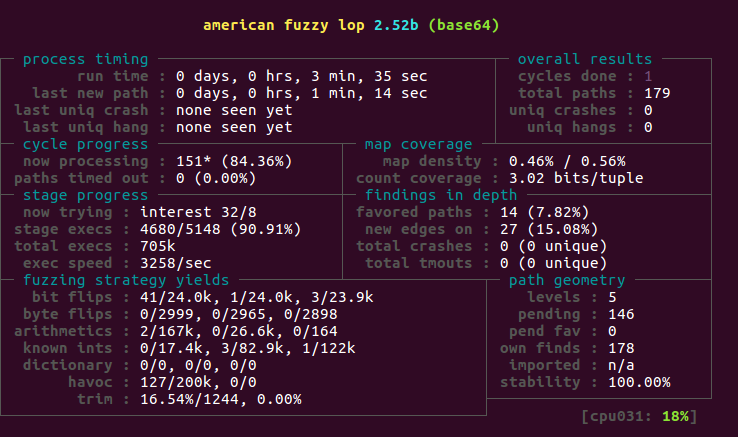
Generally speaking, the commands compile base64 with code instrumented by afl. Then, type the following command to run afl-fuzz on base64:
$ /xx/afl-fuzz -i lava_corpus/LAVA-M/base64/fuzzer_input -o ../output -t 100 -- ./base64 -d @@
The line tells afl to fuzz base64 binary, with start inputs from a folder sepecified with -i, and to save all data (status, crashes, generated seeds, etc.) to the location by -o. And it is limited to run no longer than 100 ms for each input. We use @@ to fetch input from the file and feed it directly to the program.
If you could see the following screen, it means afl is running: